Hi,
Today's Straits Times carried an article entitled "Safer Screening for Down Syndrome".
I want to share some of my own thoughts on this topic that we usually cover under the chapter on Genetics in Secondary 4 Biology.
What is Down Syndrome?
This is a chromosomal disorder or mutation that results in a child being born with 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. (The extra chromosome was incorporated into the egg cell during meiosis.) The child with this syndrome (= a host of medical problems) will usually show learning disabilities, and have thicker and shorter neck and will have other health problems.


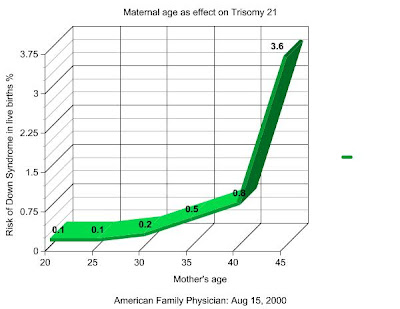
Who will give birth to Down Syndrome babies?
Pregnant women aged 35 and above are usually advised to test for DS as they have higher risk. This does not mean that younger women will not have DS babies, but just that the chances are smaller.
Why test for Down Syndrome?
Since this is a genetic disease parents would be worried of having such a child. There is no cure for this disease. The child would require more attention than a normal child and the medical costs would also be higher as the child has many health conditions that needs to be addressed. The parents must prepare for this.
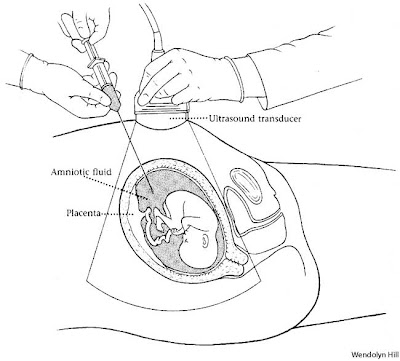
How to test for Down Syndrome and other genetic diseases?
There are many tests:
- Amniocentesis
Click on this link to view a Youtube video on how it is done by a doctor.
In this procedure a needle is inserted into the womb/uterus and some of the amniotic fluid(fluid in the "water bag" that is found around the foetus) is drawn into a syringe. The fluid contains some cells from the baby. These cells will be examined under the microscope and chromosomes will be examined and counted, (chromosome mapping). If the number of chromosomes is more than 46 or less than 46 than it indicates that the baby will probably have a genetic disease. - Chorionic villus sampling or CVS
Click on this link to view a Youtube video on how it is done by a doctor.
In this procedure a needle is inserted into the uterus and some cells of the placenta will be drawn into a syringe. The cells of the placenta, especially the villus, will be made of cells from the baby and not from the mother. Again chromosome mapping will show up the chromosome numbers and abnormalities. - Blood testing for chromosome mapping
Click on this link to view a Youtube video on how the doctor uses blood taken from the pregnant women to look for cells belonging to the foetus. Once the foetal cells are identified and isolated, chromosome mapping can again be applied to test for chromosomal abnormalities. - First Trimester Combined Screening.
This is a very new procedure that I just read about in today's ST. This procedure is better than amniocentesis and CVS as it is non invasive, ie no need to stick needles into the uterus. It includes a blood test to look for abnormal levels of certain hormones and proteins and a ultrasound scan to measure the thickness of a fluid filled tissue at the back of the foetus neck. then a computer programme is used to calculate the woman's the risk based on her age, family history, and the results of the blood test and ultra sound scan.
The FTCS test is better than the other tests for the following reasons:
- It is non invasive. There is a 1% risk of miscarriage in amniocentesis and CVS
- It is cheaper, only about $300 to $350. Amniocentesis and CVS costs more than $1000 each
- It can be done at a earlier stage of pregnancy, within 11 to 13 weeks of pregnancy.
Amniocentesis can be done between 10 to 14 weeks and CVS between 15 to 20 weeks of pregnancy - As it is non invasive and the chances of miscarriage is low, more pregnant woman would like to consider it and the detection rate is about 90%.
Click on these links to view more videos on tests during pregnancy.
Cheers





Yeah... Nowadays, many parents choose to test using the aminotic fluid to prevent genetics diseases. But.. As a person gets older, the possibility of having preg. decreases and the disease complication increases. So married young, give birth young. Find a good gene partner :P
ReplyDelete